If interested to sponsor email carlos@thevrara.com
To fill out the survey, click here
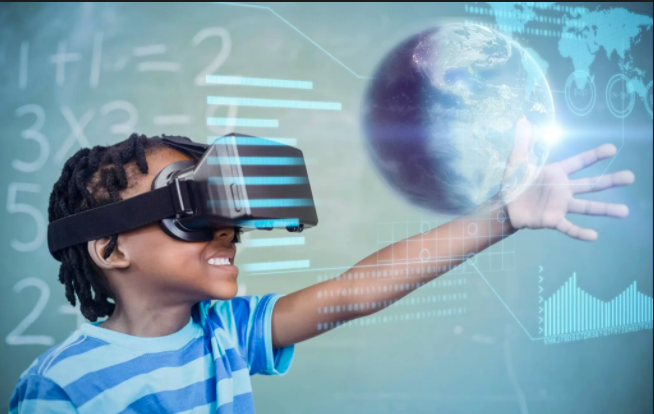
By the year 2025, immersive technologies (VR/AR) will be much more common than today. The increased interest of the large technology companies in these emerging technologies has been one of the major driving factors for the market.
The global virtual reality market size was valued at USD 7.3B in 2018 is projected to reach USD 120.5B by 2026, exhibiting a CAGR of 42%. VR market potential is very high with the full immersive VR applications, and adoptions in the industry such as education, healthcare, automotive, manufacture, defense and many others. The leading sector is anticipated to be the instruction and learning (education and training). With some creative thinking and a new immersive learning approach, training companies and colleges can do the same in disruptive environments.
As the Education Committee, we have come together globally to share best practices, reflections, experiences, case studies, meetings, failures, and celebrating our wins where collectively work together to build global standards for VR & AR technology. And today, as part of our new Mission “Jumping into the Future of VR/AR in Education, diving in Blue Oceans Vision 2025”, we have decided to start this new project.
This project began in the summer of 2017, with one primary and basic question- Do you think that VR/AR will be part of your future education ecosystem?. Additionally, we were looking for best practices in VR in Education along 2018 and some lessons learned from the very first implementations along this period. Now is time to jump into the Future.
The survey is designed to get insights, thoughts, experiences and case studies on the emerging trend of virtual and augmented reality in Education.
The final research from this survey will provide an in-depth assessment of the VR market in Education, including the following sections:
Demographics, definition, role description and location
Methodologies and experiences, describing the experience with in VR/AR technology
VR/AR Ecosystems, describing the different components
Barriers of adoption, identifying the entry barriers of adoption
Opportunities, describing the benefits and new opportunities of using VR/AR technology
About the Research
The main target of the research is to collate the State of the VR/AR Market in Education worldwide, providing great benefits to the Educational Community: providing assistance, relevant and global information, VR future roadmap, identify the major opportunities, market drivers, understand the teachers/student’s needs, IT future convergence and implementation scenarios and ecosystems. For this purpose, we want to analyze and evaluate the real situation of the technology in Education Sector and the potential of that for the next coming years.
Call for Sponsors
We are inviting sponsorship from industries, businesses, and government agencies including the leading players in VR/AR Technology.
Now it is time for sponsorship of this unique VR/AR in Education Research, and help us to promote this survey globally. We are looking for those who really believe in this independent initiative “VR/AR in Education” and want to help us to expand our Community worldwide. By sponsoring the VR/AR Education Research and Survey, you will be concretely responding to the New Disruptive Education Community call to action to end education barriers and create value from VR/AR technology for the Educational Community.
If interested to sponsor email info@thevrara.com
Call for Participation
Please take 10 minutes to answer this survey. Click here
Also, we would be very grateful to you if you can share this Call for Participation within your global network.
The survey will stay open until December 31, 2019.
Your input is very important for us and may influence the future of VR/AR tech research for the next 5 years!
The 2019 VR/AR in Education survey is an independent initiative from VR/AR Association and the Education Committee.
Regards,
Co-Chair, VR/AR Association Education Committee